The Syrian civil war is considered one of the most destructive crises in the Middle East. According to the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees, this is the most dangerous refugee crisis since World War II. It has resulted in massive internal and external population displacements.
How did it begin?
The success of the Arab Spring in Egypt and Tunisia encouraged Syrians to protest against the government and security forces in order to put an end to their abuse of power. Poverty, violations of human rights, and severe drought effects were the complementary reasons behind the protests. Insurgents occupied neighborhoods in many cities. The government used artillery, aircraft, and tanks. The unrest spread across the country, and the battle transformed from accountability to gaining absolute power. The West was shocked at this large-scale bloodshed. It provided assistance to opposition groups to make the government come to the table. Meanwhile, the government’s supporters are the obstacle in this way.

Various Factions in the War
There are various factions participating in the war, which makes this crisis complex and difficult to resolve.
The Government
The whole Syrian civil war is associated with the removal of President Bashar al-Assad. Bashar al-Assad belongs to the Shia sect of Islam, while 83% of the population of the country is Sunni, which gives a color of extreme sectarianism to this conflict. The regime is being backed by Iran, Russia, and China (diplomatically).
Moderate Rebels
This group was formed by the Free Syrian Army and demanded the removal of Assad from power. This group is supported by the US, the Gulf States, Turkey, and Jordan.
Radical Opposition in the Syrian civil war
This faction is presented by Jabat al-Nusra, a branch of Al-Qaeda that changed its name to Jamat Fateh al-Sham. This group demands the removal of the government and the imposition of conservative Islamization. The radical opposition is backed by Saudi Arabia and Qatar.
ISIS\ISIL\IS\Daesh
Iraqi and Syrian Islamic States—Latvia was associated with al-Qaeda but later broke away. The US and Israel are allegedly supporting Daesh.
Kurds
It is an ethnic group that originated in the northern parts of Syria and Iraq and is semi-autonomous in the southern and eastern parts of Turkey. The Syrian Democratic Forces are the Kurdish defense force. YPG International, or the People’s Protection Unit, operates in Iraq and Syria. The Kurdistan Workers’ Party works in Turkey. Both are components of the SDF. Foreign countries’ aid and assistance are playing a major role in prolonging this war.
Government Supporters and Acquired Territories
Iran and Russia are the two major supporters of Assad. Iran provided 80,000 militants to save Assad’s government. General Qasim Soleimani, commander of the IRGC, was instrumental in recapturing lost territories. It was he who convinced Russia to get into the war. Russian airstrikes strengthened Assad’s regime to a great extent. Involvement in this war boosted Russian arms sales to $15 billion in 2015. The main interest of Iran in the conflict is to gain strategic depth against Israel. About two-thirds of the country is under the control of the Syrian government. All major cities, including Damascus, Latakia, Hama, Homs, Aleppo, and Deraa, are occupied by government forces.
The territory occupied by Kurds
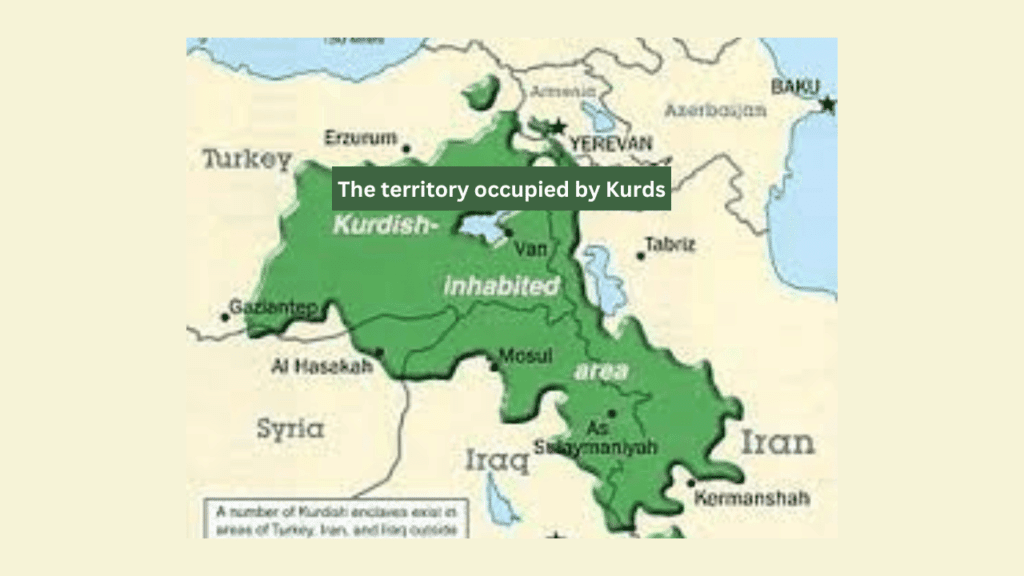
The Syrian Democratic Forces control the country’s northeast. It seized territory previously controlled by IS, including the Hasaka governorate, Raqqa north of the Euphrates, and parts of the Deir Ez Zor governorate.
Turkish-occupied Area
Turkey has occupied northern Syria since 2016. This area is isolated and vulnerable.
Failed peace talks
The international community, especially America, arranged Geneva Peace Talks I and II in 2014 and 2016, respectively. These failed. It was because Assad does not want his presidency to be discussed. He believes that he could get more territory with the help of Iran and Russia than through table talks.
Critical Analysis
Some analysts are of the view that the US strategy for bringing Assad to the table talks with the help of limited military pressure and the UN is mistaken. Assad will never compromise his position. In fact, genuine power sharing is also unacceptable for him and his allies. Because of their occupation of major cities, Assad and his allies can afford to prolong the crisis.
Syrians are suffering a lot of hardships because of this war. The majority of the population has fled the country, while others are barely surviving. It is the need of the hour to resolve this issue as soon as possible with the combined efforts of the international community and international organizations.





3 Comments on “Syrian Civil War In The Middle East”